Fisheries play a critical role in global food security, providing essential protein and nutrients to billions of people worldwide. Sustainable fisheries management is key to ensuring that these resources remain available for future generations. This page explores how fisheries contribute to food security and the features that support this vital connection.
Why Fisheries Matter for Food Security
Fish are an important source of high-quality protein, omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins, and minerals. For many communities, particularly in developing countries and coastal regions, fish is a staple food and a primary source of nutrition. When managed sustainably, fisheries can provide a reliable and affordable source of food, contributing significantly to food security and reducing malnutrition.
Direct Contributions to Food Supply
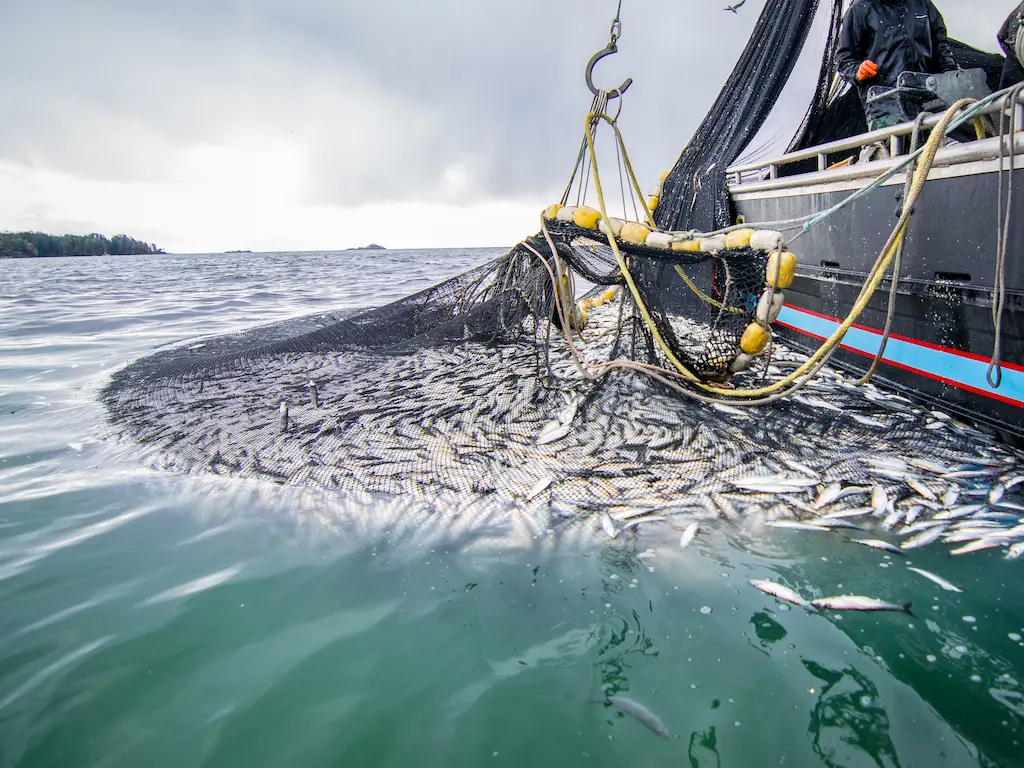
Fish directly contribute to the food supply through both wild capture fisheries and aquaculture (fish farming). Wild capture fisheries harvest fish from natural environments like oceans, rivers, and lakes. Aquaculture, on the other hand, cultivates fish in controlled environments.
Economic Benefits and Livelihoods
Beyond direct food provision, fisheries also support the livelihoods of millions of people involved in fishing, processing, distribution, and related industries. A healthy fisheries sector contributes to economic stability and food access, especially for coastal communities.
Key Features Supporting Food Security Through Fisheries
Several factors contribute to the effectiveness of fisheries in supporting food security. These include sustainable management practices, responsible fishing techniques, and equitable distribution systems.
| Feature | Description | Impact on Food Security |
|---|---|---|
| Sustainable Fisheries Management | Implementing regulations and policies to prevent overfishing and protect fish populations. This includes setting catch limits, managing fishing gear, and establishing marine protected areas. | Ensures long-term availability of fish stocks, safeguarding food supply for future generations. |
| Combating Illegal, Unreported, and Unregulated (IUU) Fishing | Enforcing regulations to prevent illegal fishing activities that deplete fish stocks and undermine sustainable management efforts. | Protects fish populations from unsustainable exploitation, preserving food resources. |
| Promoting Aquaculture | Developing sustainable aquaculture practices to supplement wild capture fisheries and increase fish production without harming the environment. | Provides an alternative source of fish, reducing pressure on wild stocks and increasing food availability. |
| Improving Post-Harvest Handling and Distribution | Implementing efficient processing, storage, and transportation methods to reduce spoilage and ensure that fish reaches consumers in good condition. | Maximizes the availability of edible fish and minimizes waste, contributing to greater food security. |
| Supporting Small-Scale Fisheries | Empowering small-scale fishers and fishing communities through access to resources, training, and market opportunities. | Enhances the livelihoods of vulnerable populations and ensures equitable access to food resources. |
| Climate Change Adaptation | Implementing strategies to mitigate the impacts of climate change on fisheries, such as adapting fishing practices, protecting coastal habitats, and managing fish stocks resilient to changing ocean conditions. | Maintains the resilience and productivity of fisheries in the face of climate change challenges, ensuring continued food provision. |
The Importance of Collaboration
Effective management of fisheries for food security requires collaboration among governments, fishing communities, scientists, and other stakeholders. By working together, we can ensure that fisheries continue to play a vital role in nourishing the world’s population.
Further Resources
This information is intended for educational purposes and should not be considered as professional advice.